Case Converter
Case Converter is located under Textual Analysis in Pre Processing, in the task pane on the left. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
A case converter is used to adjust the capitalization in a textual document. It can alter the case of an alphabet to a lower case or an upper case. It is used for preprocessing textual data only.
Properties of Case Converter
The available properties of Case Converter are shown in the figure below.
The table given below describes different fields present in the properties of the case converter.
Field | Description | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Run | It allows you to run the node. | - | |
| Explore | It allows you to explore the successfully executed node. | - | |
| Vertical Ellipses | The available options are
| - | |
Task Name | It displays the name of the selected task. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Text | It allows you to select the text for which you want to convert the case. |
| |
| Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control over the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
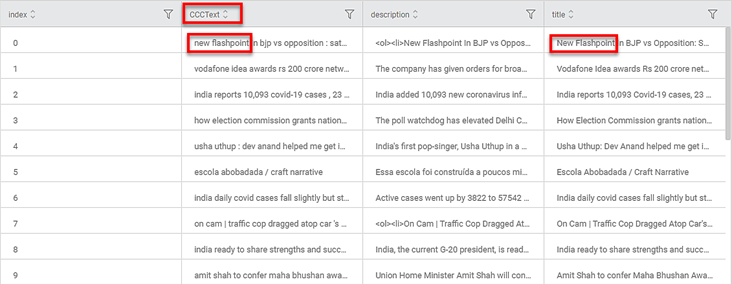
Interpretation of Case Converter
In the figure, the column heading text represents the text after the Case Converter has been applied.
In the highlighted example, the word 'New Flashpoint' has been lowered to 'new flashpoint'.
Related Articles
Case Converter
Case Converter is located under Textual Analysis in Pre Processing, in the task pane on the left. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis. A case ...Configuring RubiAI Model in Administrator Application
RubiAI Model Configuration allows administrators to connect Rubiscape with Large Language Model (LLM) providers such as Gemini. Once configured, RubiAI features become available across Rubisight and Rubistudio for Designer Assistant, widget insights, ...View Log Screen Enhancement
1. Introduction The View Log screen enhancement provides improved filtering, sorting, and workflow-specific visibility within the log panel. These improvements enable users to efficiently analyze workflow and node-level execution details. 2. Feature ...Export to PDF/PPT using Dashboard Schedule
In RubiSight, you can export a dashboard using the Export functionality. Refer to Exporting a Dashboard. You can not only schedule this export, but also send the dashboard pages as PDF via email, at a stipulated date and time. Notes: You can schedule ...Batch Processing
Pipeline allows you to divide the dataset/Tasks into batches and then process it. Batch processing is mainly used to simplify many ETL operations like Missing value Imputation, expression, and validating data. You can specify the batch size called ...