Managing Things
Understanding Things
A thing in RubiThings is any physical object, such as an intelligent sensor or edge device that can transfer data over a network, any of the IoT-enabled devices
Adding a New thing
You can add a thing by
- Clicking Things in the Manage dropdown (for the first time).
- Clicking Create Thing on the top-right corner of the Things page (after you have added a thing).
- Clicking Add Things from the Create (
 ) menu present on the Title pane.
) menu present on the Title pane.
To add a thing,
- In the Manage dropdown, click Things. A Things page is displayed.
- Click Create Thing (
 ) on the top-right corner of the Things A Create New Thing page is displayed.
) on the top-right corner of the Things A Create New Thing page is displayed. - Enter a suitable Name for the Thing. This field is mandatory.
- From the Select Payload Type dropdown, select one of the payload data types.
Structured Data: It is most commonly classified as quantitative data. Structured Data is form of data with which most of us are familiar. Consider data in relational databases and spreadsheets that fits nicely into specified fields and columns.
Names, dates, addresses, credit card numbers, stock information, geolocation, and other types are the examples of structured data. It contains numbers, Booleans, and strings.
Unstructured Data: It is typically classified as qualitative data. Unstructured Data cannot be handled or evaluated using traditional data tools and methodologies.
Text, bytes, video files, audio files, mobile activity, social network posts, satellite photography, surveillance imaging, and so on are all examples of unstructured data. - From the Protocol dropdown, select the correct protocol to be assigned to the Thing. This field is mandatory. Read the Note below for more information on protocols and the available protocol types.
- From the Data Template dropdown, select a data template to be assigned to the Thing. Make sure to set the correct data template. This field is mandatory.
- Enter a suitable Tag for the Thing. This field is mandatory. Read the Note below for more information on an example of tags.
- From the Location dropdown, select the correct location of the Thing.
- Enter the correct IP Address to which the Thing is connected. This field is required if files are exchanged between the publisher and subscriber systems.
Currently, the IP address is not being used for file transfers. Hence, this field is not now mandatory. - Enter the Model Number for the Thing.
- Enter a suitable Description for the Thing.
- In Show Inactive After (Minutes), enter the time in minutes.
Click Create.
The Thing is created and added to the list on the Things page.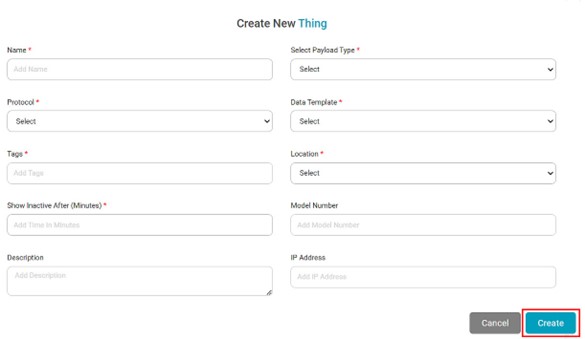

Notes- An IoT communication protocol is a communication mode to safeguard optimum data security for the exchange between IoT-enabled and connected devices.
- All IoT devices are generally connected to the Internet via the IP (Internet Protocol) network.
- Following is the list of protocols available in RubiThings.
- MQTT
- COAP
Tags are the keywords that classify the Things under group.
For example, consider a Things that records the temperature of various locations. Another Thing detects light at different locations. In this example, you can add tags like 'Temperature' and 'Light Detector' to the two things while creating them.
You can use these tags to organize the Things under a group.
One group can contain many things.
- After creating a Thing, its default status is "Inactive." The customer shares the data over a common platform. When we subscribe to the data, the status changes to "Active."
Searching Thing
Searching a thing from a long list can be time-consuming. The Search field helps to search for your desired Thing quickly.
To search for a thing,
- In the Manage dropdown, click Things.
- Type the name of the Thing you want to search.
Partial names are allowed for searching. A list of thing names matching the search string is populated as you start typing.
For example, in the image below, as we type the string "De," the Thing results with the same string are populated on the dashboard.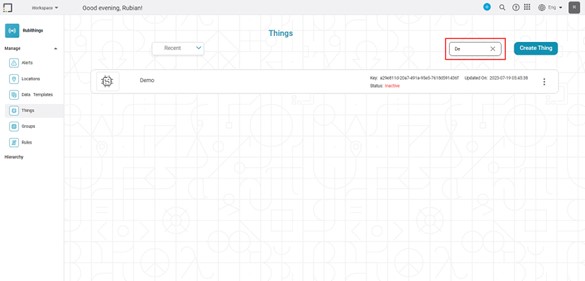
Sorting Things
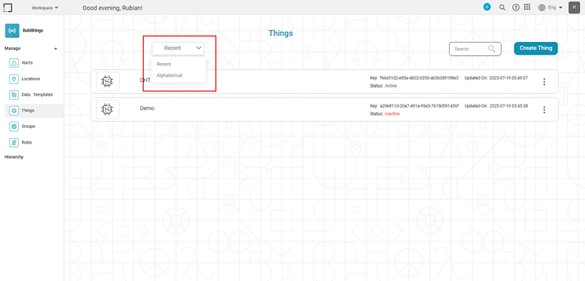
The Things are sorted by the date and time they were created, with the most recent Thing appearing first. You can also sort things according to alphabetical order.
To sort things,
- In the Manage dropdown, click Things.
- Click Recent near the top-right corner.
- Select Alphabetical. The list is sorted in alphabetical order.
Editing Thing
To edit a thing,
- In the Manage dropdown on the home page, click Things.
- Identify the Thing you want to edit.
- To navigate to the Edit Thing page, hover over the Thing and click the Edit icon (
 ). Alternately, you can click on the Thing and then click the Edit icon (
). Alternately, you can click on the Thing and then click the Edit icon ( ) on the next page.
) on the next page. - On the Edit Thing page, make the necessary changes to the various fields.
Click Update. Your Thing is saved with the updated information.
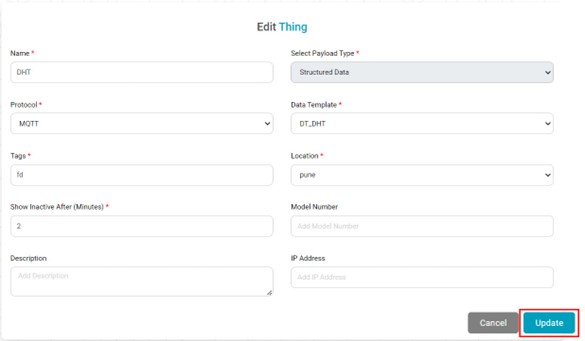

Notes- Out of the various fields, the Data Template field is not available for editing. Once assigned, you cannot change the Data Template assigned to a thing.
- For example, the data template "Pressure" assigned to "Query3," as seen in the figure above, cannot be changed.
Deleting Thing
You can delete a thing that is no longer required or active.
To delete a thing,
- In the Manage dropdown on the home page, click Things.
- Identify the Thing you want to delete.
- Hover over the Thing and click the Delete icon (
 ). A confirmation message to delete the Thing pops up.
). A confirmation message to delete the Thing pops up. - Click Delete on the message. The Thing is deleted, and a confirmation message is displayed.
Related Articles
Managing Groups
Understanding Groups A group in RubiThings is to organize your things dynamically into logical groups by tagging them. Adding a Group You can add a group by Clicking Groups in the Manage dropdown (for the first time) Clicking Create Group on the ...Hierarchy of Things
Understanding Hierarchy A hierarchy in RubiThings is the visualization mode of locations and their constituent things. Understanding the Hierarchy Home Page The RubiThings Hierarchy page is shown below. The Hierarchy Page displays a list of all ...Managing Datasets
What is Reader In rubiscape, a reader is referred to as a dataset. Dataset is a collection of elements extracted from different sources that can be integrated into one. The datasets added can be shared across different Projects. They are used to ...Managing Rules
Understanding Rules A rule in RubiThings is a set of instructions defined to trigger and generate an alert based on the specified condition. These rules get applied to any data packet in near real-time. Adding a Rule You can add a rule by Clicking ...Managing Workflows
You can schedule workflows to run at pre-decided time intervals as an administrator. The scheduled workflows execute at the set time without any user intervention. It makes the automation of certain processes easier. You can Create new schedules Run ...