Isolation Forest
Isolation Forest is located under Machine Learning ( ) in Anomaly Detection, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method (or double-click on the node) to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
) in Anomaly Detection, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method (or double-click on the node) to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Isolation Forest.
Properties of Isolation Forest
The available properties of the Isolation Forest are as shown in the figure given below.
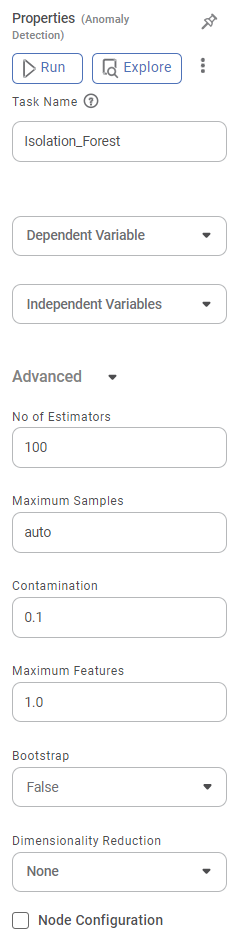
The table given below describes the different fields present on the properties pane of Isolation Forest.
Field | Description | Remark | |
| Run | It allows you to run the node | - | |
| Explore | It allows you to explore the successfully executed node. | - | |
| Vertical Ellipses | The available options are
| - | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Dependent Variable | It allows you to select the dependent variable. |
| |
Independent variables | It allows you to select the experimental or predictor variable(s). |
| |
Advanced | No of Estimators | It allows you to select the number of base estimators in the ensemble. |
|
Maximum Samples | It allows you to select the maximum number of samples. |
| |
Contamination | It allows you to enter the proportion of outliers in the data set. |
| |
Maximum Features | It allows you to select the minimum number of features. |
| |
Bootstrap | It allows you to select a bootstrap value of either True or False. |
| |
Dimensionality Reduction | It allows you to select the dimensionality reduction technique. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) maps the data linearly to a lower-dimensional space to maximize the variance of the data in the low-dimensional representation. |
| |
Variance | It allows you to enter the variance value. |
| |
Example of Isolation Forest
Consider a Credit Card dataset with 400 records. A snippet of input data is shown in the figure given below.
In the Properties pane of Isolation Forest, the values selected are given in the table below.
Property | Value |
Dependent Variable | Student |
Independent Variables | Age and Balance |
No. of Estimators | 100 |
Maximum Samples | auto |
Contamination | 0.1 |
Maximum Features | 1 |
Bootstrap | False |
Dimensionality Reduction | None |
The Result page of the Isolation Forest is shown in the figure given below.
The Result page initially displays the Cluster Plot based on the default combination of features in the X-axis and Y-axis data fields. To plot a Cluster Plot for different combinations of features, select the respective features from the X-axis and Y-axis drop-downs.
Note: | If you try to plot the Cluster Plot with the same features in the X-axis and Y-axis data fields, then Rubiscape gives an error. |
You can also view the Confusion Matrix based on the Event of Interest states of the selected dependent variable. Here, the dependent variable selected is Student, and its Event of Interest states are No and Yes.
To view the Confusion Matrix,
- Select either of the values from the Event of Interest drop-down.
- Click Evaluate, located in the top-right corner.
The Confusion Matrix is displayed on the right-hand side of the Result page.
The coloured boxes in the Confusion Matrix represent the predicted values, while the white boxes represent the error values.
Notes: |
|
The output Data page displays one additional column of Label along with the existing 13 features in the Isolation forest result. A snippet of the output data of 14 columns, displayed on the Data page, is shown in the figure below.
Notes: |
|
Interpretation of Result of Isolation Forest
The figure given below shows the Cluster Plot on the Isolation Forest Result page.
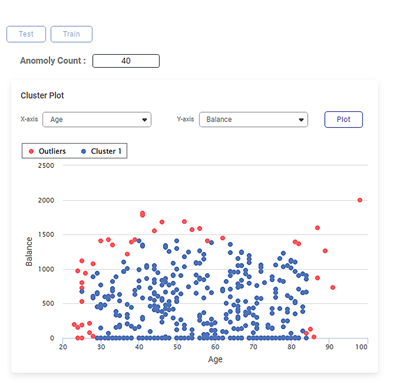
Some of the key observations from the Cluster Plot are listed below.
- The independent variable or label selected in the X-axis data field is
- The independent variable or label selected in the Y-axis data field is Balance.
- The Cluster Plot is plotted between the two labels, one on X-axis (Age) and the other on Y-axis (Balance).
- The blue dots in the plot represent the non-outlier/normal data points in the dataset of 400 data points.
- The red dots in the plot represent the outliers in the cluster of data points.
The figure given below shows the Confusion Matrix displayed on the Isolation Forest Result page.
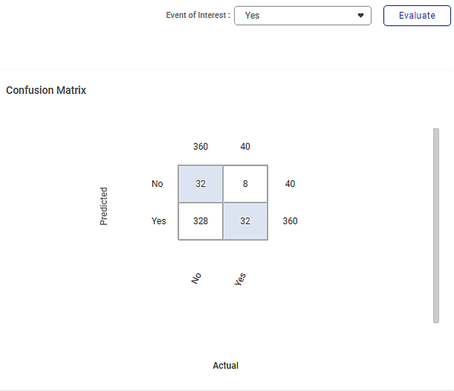
Some of the key observations from the Confusion Matrix evaluated for the selected dataset (of 400 data points) are listed below.
- The Confusion Matrix is evaluated for the value No selected from the Event of Interest drop-down.
- The blue boxes represent the predicted values.
- The white boxes represent the error values.
The table below briefly explains what the values in each of the quadrants of the Confusion Matrix
Quadrant
Quadrant Value
Description
First (blue)
32
The predicted values of No out of the actual No values (360).
Second (white)
8
The error values of Yes out of the actual Yes values (40).
Third (white)
328
The error values of No out of the actual No values (360).
Fourth (blue)
32
The predicted values of Yes out of the actual Yes values (40).
- The value 360 represents the number of data points in a non-outliers/cluster density in the dataset of 400 points.
- The value 40 represents the number of local outliers in the cluster density in the dataset.
Notes: |
|
You can click Publish in the top-right to publish the isolation Forest task as a model. The model can be reused in a workbook for training and experimenting or used in a workflow for production.
For more information on publishing a task, refer to Publishing Models.
Related Articles
Random Forest
Random Forest is located under Machine Learning ( ) in Classification, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method (or double-click on the node) to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties ...Random Forest Regression
Random Forest Regression is located under Machine Learning ( ) > Regression > Random Forest Regression Use the drag-and-drop method (or double-click on the node) to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different ...Classification
Notes: The Reader (Dataset) should be connected to the algorithm. Missing values should not be present in any rows or columns of the reader. To find out missing values in a data, use Descriptive Statistics. Refer to Descriptive Statistics. If missing ...MLOPS - Machine Learning Operations
Introduction: Why Rubiscape MLOps? Rubiscape MLOps provides an end-to-end environment for building, tracking, publishing, and serving machine learning models. It ensures experiment reproducibility, streamlined deployment, and centralized model ...