MySQL
Creating MySQL Dataset
To create a MySQL dataset, follow the steps 1 and 2 given in Creating SQL Dataset.
The following figure shows the Product Selection page.
The Data Connect page for choosing your dataset type is displayed.
From the RDBMS options, select MySQL.
The following figure shows RDBMS options.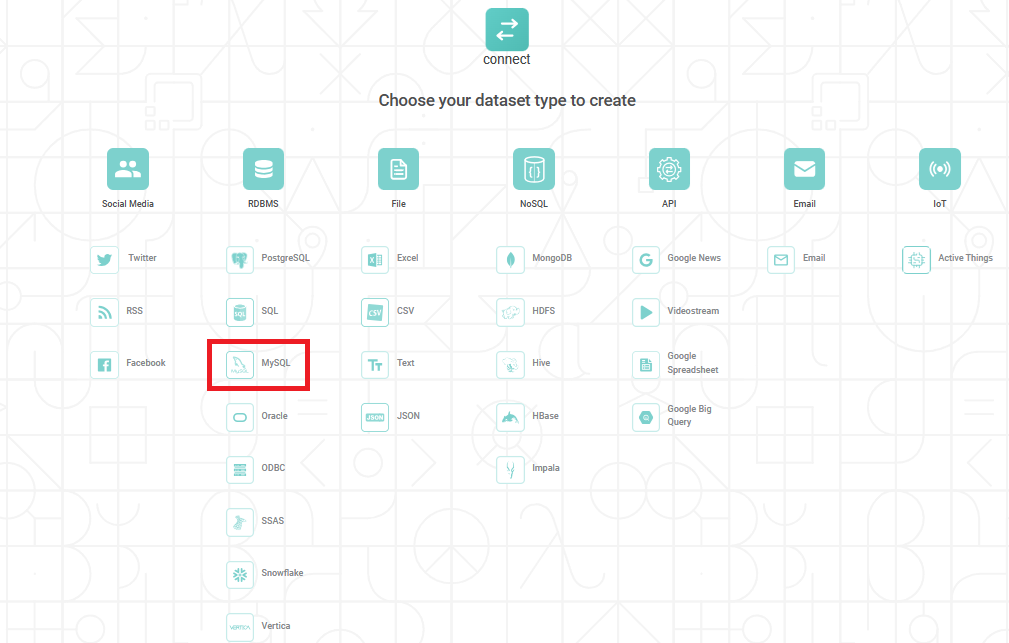
Create MySQL Dataset page is displayed.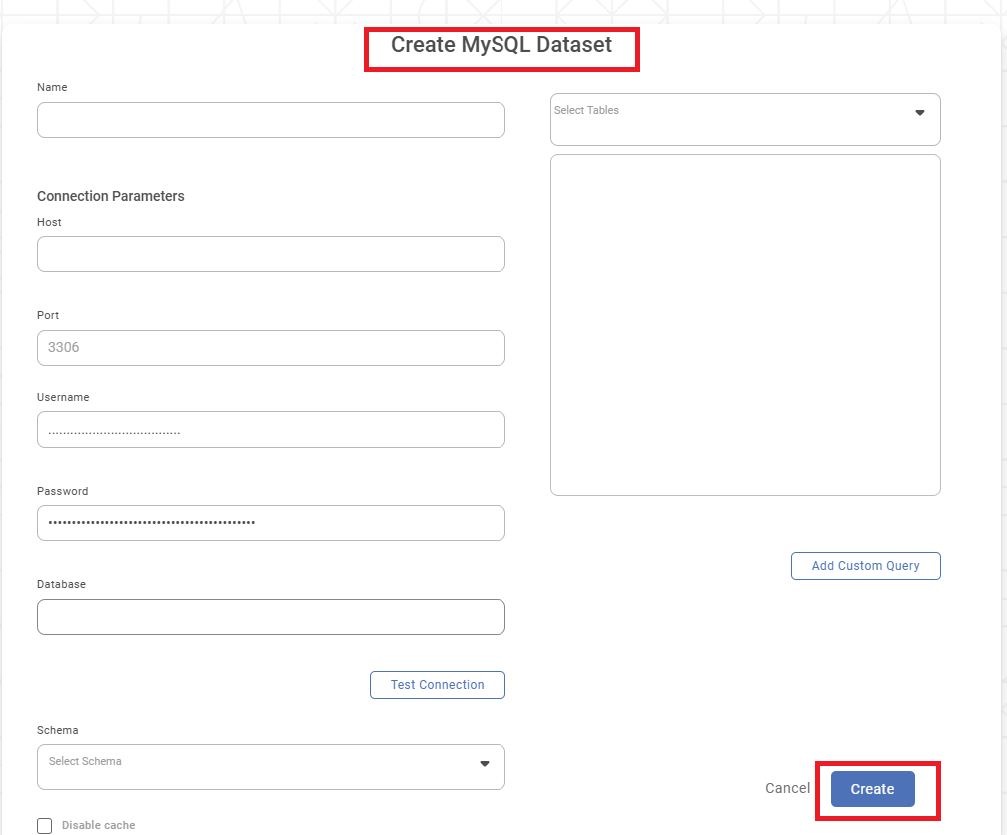
- Enter a suitable Name for the Dataset.
- In the Connection Parameter section, enter the following details.
-- Host (IP address of the server where your database resides)
-- Port (for the localhost on which the MySQL database service is available)
-- Username (of the account authorized to access the database)
-- Password (for the account)
-- Database (name to access schema(s) and the table(s) - Click Test Connection. The message "Database Connection Successful" is displayed in green if the parameters are accurate. After a successful connection, the Database dropdown is populated with a list of available databases.
- From the Schema dropdown, select the schema(s) that contains your table(s) and click Done. After selecting the schema(s), the Select Tables dropdown is populated with a list of all available tables in the schema(s).
- From the Select Tables dropdown, select the required tables and click Done.
- To add a custom query to select data from the tables, click Add Custom Query. Add Custom Query screen is displayed. Refer to Adding A Custom Query for details.
- Click Create. The MySQL dataset is created in Rubiscape and is available for use in your workbooks and workflows.
Notes: |
|
Related Articles
ODBC
Creating ODBC Dataset To create any RDBMS or Non-RDBMS Dataset using ODBC, follow the steps 1 and 2 given in Creating SQL Dataset . The following figure shows the Product Selection page. The Data Connect page for choosing your dataset type is ...RubiSQL
RubiSQL is a feature within Code Fusion that helps write code in SQL to modify the values in your database. It also allows you to delete values in your database. You can use the RubiSQL node as a stand-alone node or connect it to the Reader node ...RubiSQL
RubiSQL is a feature within Code Fusion that helps write code in SQL to modify the values in your database. It also allows you to delete values in your database. You can use the RubiSQL node as a stand-alone node or connect it to the Reader node ...Writing Data to the Template Table
You can store the result of algorithm flow or the Reader to a dataset table. Note: You can write to an RDBMS or ODBC (SQL, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle) datasets only. To write the output data to a template table, follow the steps given below. Build ...Writing into Template Table
You can store the result of algorithm flow or the Reader to a dataset table. Note: You can write to an RDBMS or ODBC (SQL, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle) datasets only. To write the output data to a template table, follow the steps given below. Build ...