RubiR
RubiR is a feature within Code Fusion on the Rubiscape platform to write your code in the R programming language for building models.
You can use RubiR as an independent node or connect it to your Reader node (dataset) or other algorithm nodes.
Notes: |
|
Writing Custom Code using RubiR
To write your custom code using RubiR, follow the steps given below.
- Create your algorithm flow. Refer to Building Algorithm Flow in a Workbook Canvas.
- Drag and drop RubiR on your workbook/Pipeline canvas.
Connect RubiR to the required node in your algorithm flow.

Notes:
- You can connect a reader to RubiR but cannot access any of the features of the reader.
- Alternatively, you can use RubiR as a stand-alone node without connecting to any other node.
- Select RubiR and in the Properties pane, click Configure.
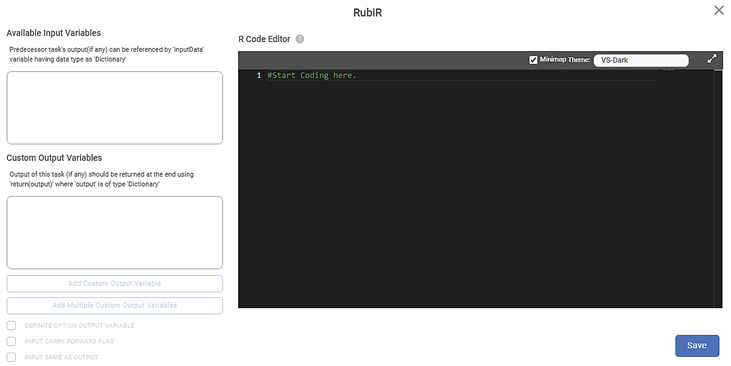
The fields/icons on the R configuration page are described in the table below.
Icon/Field
Description
Available Input Variables
- It displays the features (columns) present in the preceding task’s output. These features are stored in a variable named
inputData, which is of dictionary data type. - Dictionary is a data type that contains name-value pairs.
- You can access the features in the
inputDatavariable and process them to create your custom variables. - You can access all the features (columns) present in the preceding task and the index of each row in the
inputData[]variable. - You can access a single feature (column) from the features present in a particular preceding task and the index of each row in the
inputData[‘<column_name>’]variable.
Custom Output Variables
Currently Not available in RubiR.
R Code Editor
The R Code Editor helps you to enter your customized R code. Refer to Using R Code Editor.
TRAINING REQUIRED
Functionality is coming soon.
Minimap - It is a small, scaled version of code editor window.
- If selected, shows the overview of entire code area in top right corner of code editor window.
Theme - It helps you to customize the code editor theme.
- Following theme options are provided:
- VS-Dark
- VS-Light
- High Contrast-Dark
- High Contrast-Light

It helps you to maximize the Code Editor page.
It saves the changes, closes the configuration page, and returns you to the workbook canvas
- It displays the features (columns) present in the preceding task’s output. These features are stored in a variable named
- Write your R code in the R Code Editor. Refer to Using R Code Editor.
- Click Save.
- To execute the code, Run the RubiR node.
After successful execution, a confirmation message is displayed. You can view the output of the custom component under View Log > Custom Component Log.
- The input variables are stored in the form of a Dictionary data type inputData.
- To print to the console, use
print().
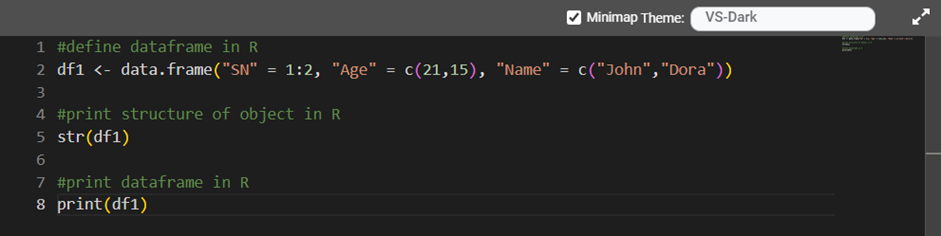
Line of Code | Result |
df1 <- data.frame("SN" = 1:2, "Age" = c(21,15), "Name" = c("John","Dora")) | It creates a data frame with the name x using the provided data. |
Str(df1) | It displays the internal structure of the df1 object. |
Print(df1) | It prints the data frame. |
Writing Custom Functions to Access Data using RubiR
You can use custom functions in RubiR to
- upload file to cloud storage
- download file from cloud storage
The following sections explain these custom functions.
Uploading File to Cloud Storage
RubiR provides a custom function to upload files to the S3 server. The code syntax to upload a file to cloud storage is shown below.
|
Downloading File from Cloud Storage
RubiR provides a custom function to download files stored on the S3 server. The code syntax to download a file from cloud storage is shown below.
|
The syntax to read the contents of the downloaded file is given below.
|
Publishing RubiR Code
You can publish the RubiR code from a workbook/Pipeline and reuse it in another workbook or Pipeline. This feature is similar to publishing models in RubiStudio.
To publish RubiR code, follow the steps given below.
- Write the RubiR code as required. Refer to Writing Custom Code using RubiR.
- Run the RubiR node.
- After the node is successfully executed, select the node, click the vertical ellipsis (
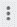 ), and click Publish code.
), and click Publish code.
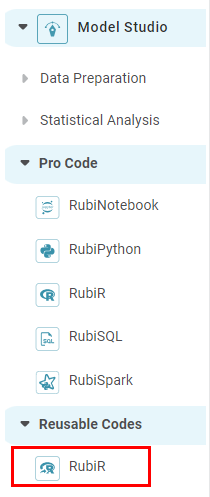
After the code is successfully published, a confirmation message is displayed. This code is listed under Reusable Codes on the Rubiscape Home page.
Notes: |
|
Reusing RubiR Code
The published RubiR code is available for reuse in workbooks and pipeline in the same workspace.
To reuse a published code, follow the steps given below.
- Open the workbook/Pipeline or create a workbook/Pipeline. Refer to Opening a Workbook and Creating a Workbook.
- Click Reusable Codes under Code Fusion in rubistudio in the Task Pane.
The available reusable codes are displayed as shown in the figure below.
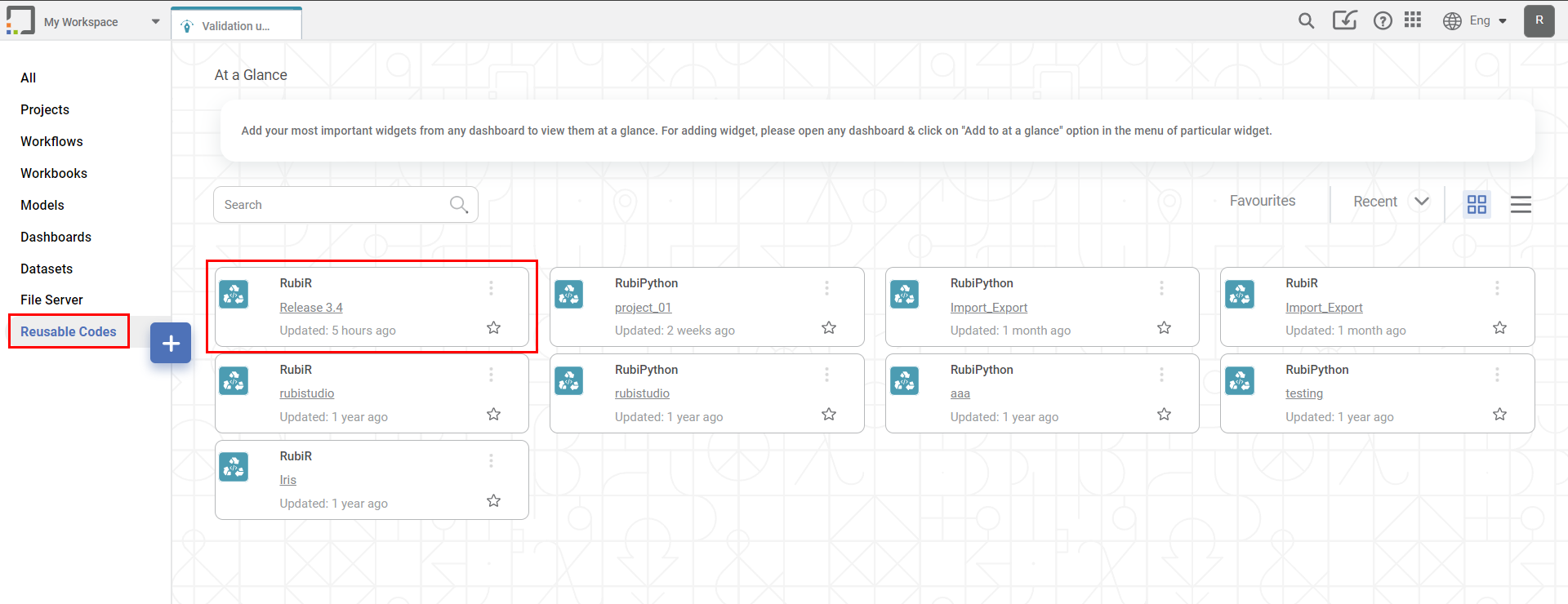
- Double-click or drag-and-drop the node on the workbook canvas.
- To run the code, select the node, click the vertical ellipsis (
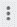 ), and click Run.
), and click Run.
Related Articles
RubiR
RubiR is a feature within Code Fusion on the Rubiscape platform to write your code in the R programming language for building models. You can use RubiR as an independent node or connect it to your Reader node (dataset) or other algorithm nodes. ...Resuable Rubipython/RubiR Code
Resuable RubiPython/RubiR Code You can publish the RubiPython/RubiR code from a workbook/Pipeline and reuse it in another workbook or pipeline of same project. This feature is similar to publishing models in RubiStudio. Note that same functionality ...Setting Variable Values from Scheduled Pipeline Execution
This functionality allows users to assign specific values to pipeline variables at the schedule level. When a pipeline runs through a schedule, the variable values defined in that schedule override the global variable values. This enables dynamic, ...
