Text
Creating Text Dataset
To create a Text dataset, follow the steps given below.
- On the home page, click Create icon .
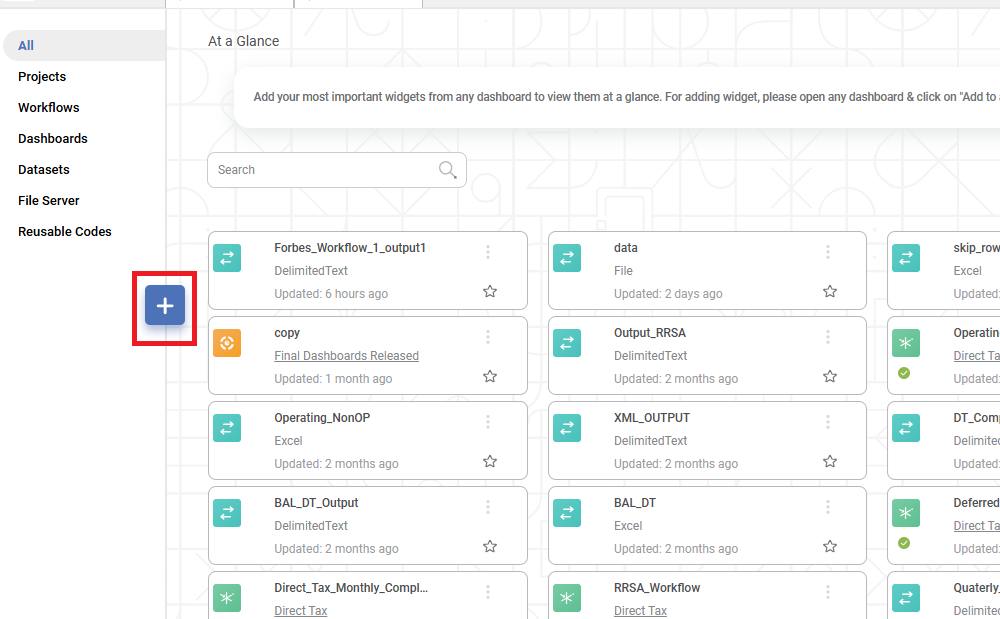
The Product Selection page is displayed. - Hover over the Data Connect tile and click Create Dataset.
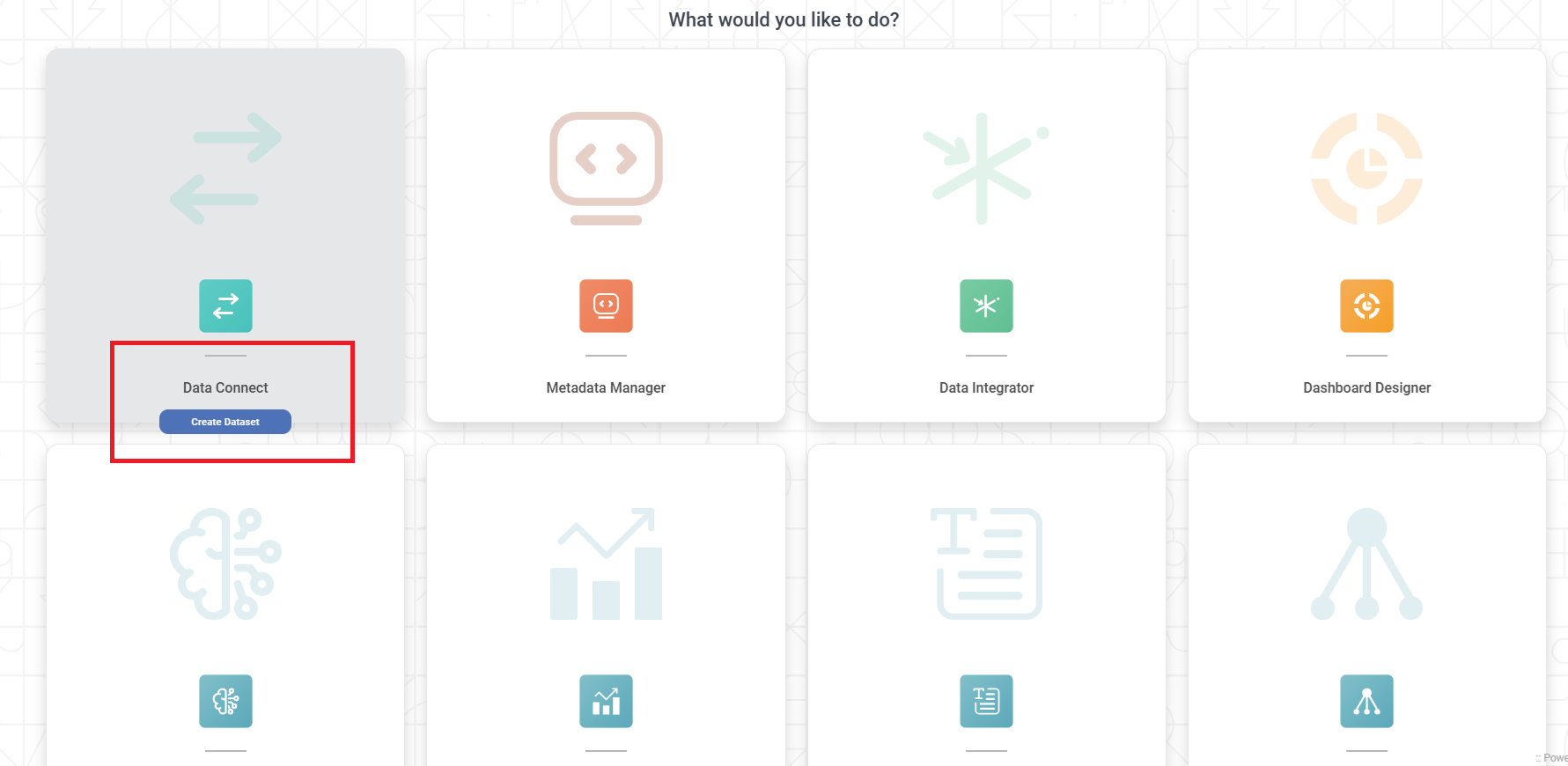
Dataset Selection page is displayed.- From the File options, select Text.
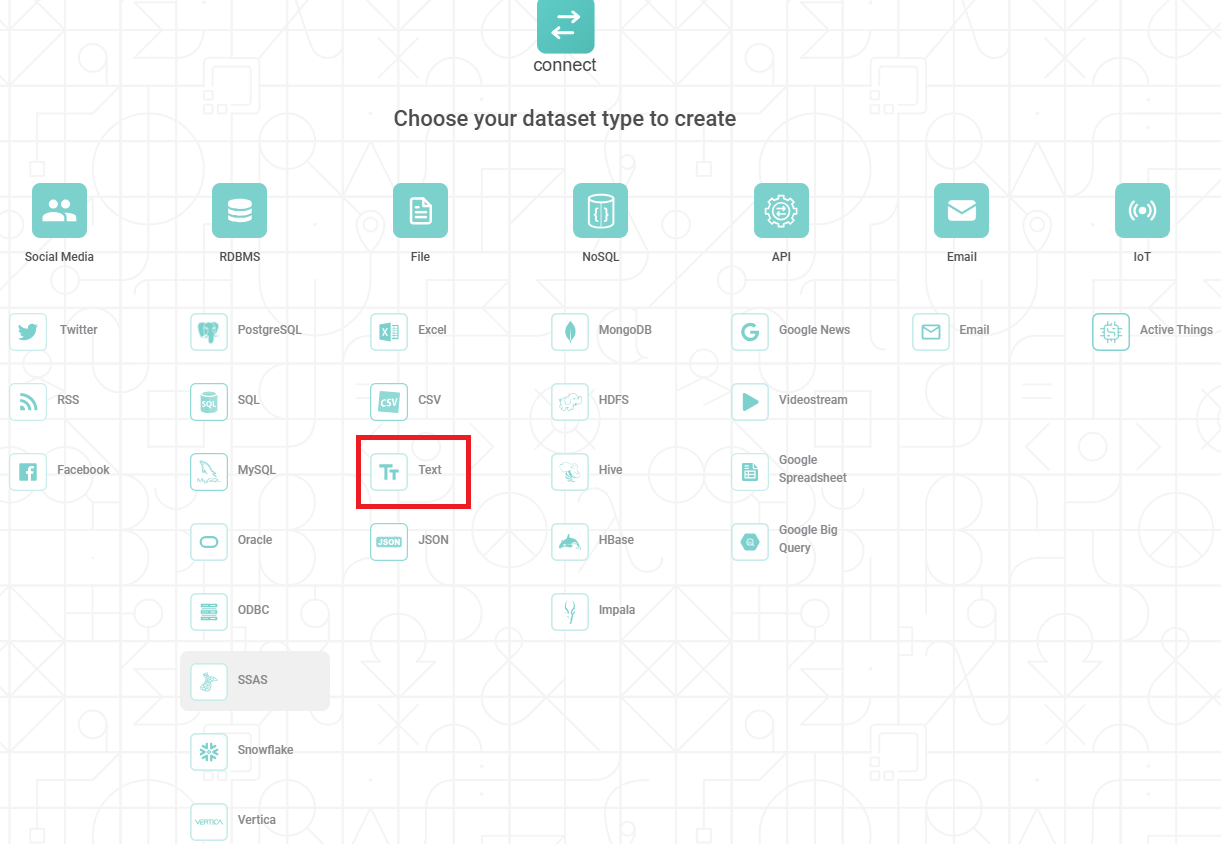
Create Text Dataset page is displayed.
- From the File options, select Text.
You can use a Text file stored on your computer or from the AWS S3 storage network to create a Text dataset. The dataset creation for these types is explained in the sections below.
Creating Text Dataset by Uploading Text File
To create a Text dataset by uploading a Text file from your computer, follow the steps given below.
- Follow steps 1 to 3 of Creating Text Dataset.
- Enter Name and Description for your dataset.
Select the Data Delimiter from the drop-down or provide a new delimiter of your choice.
Notes:
Currently, you can select the following delimiters from the drop-down:
- Semicolon
- Pipe
- Comma
- Tab
- Space
- To upload a Text file from your computer, select the Upload Text File radio button.
- Click Browse.
The File Browser window is displayed. - Browse to your file location and select a Text file.
The Features (columns) in the worksheet are displayed in the Features box. - To change the datatype of the features, refer to Configuring Feature Type.
- If you wish to remove any of the features, hover over the feature name, and click the Close icon (
 ).
).
- Click Create.
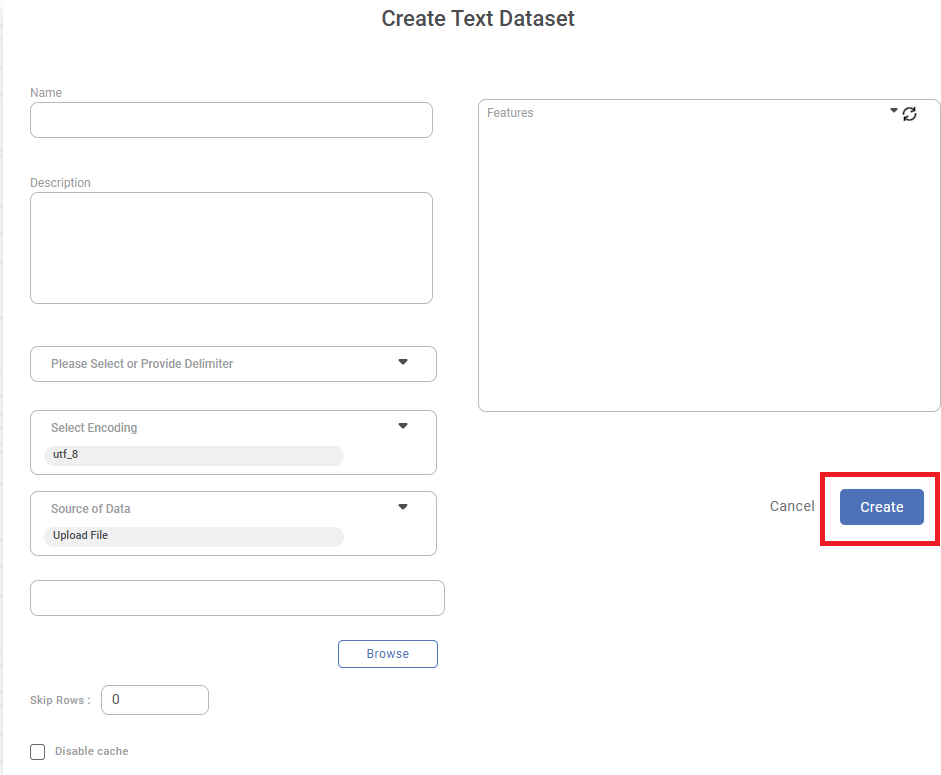
A confirmation message is displayed.
The Text dataset is created in the current workspace and available in workbooks, workflows, and dashboards.
|
Creating Text Dataset using S3 Bucket Storage
To create a Text dataset by uploading a Text file from the AWS S3 bucket storage, follow the steps given below.
- Follow steps 1 to 3 of Creating Text Dataset.
- Enter Name and Description for your dataset.
Select the Data Delimiter from the drop-down or provide a new delimiter of your choice.
Notes:
Currently, you can select the following delimiters from the drop-down:
- Semicolon
- Pipe
- Comma
- Tab
- Space
- To upload a file from AWS storage, select the S3 radio button.
A new set of dataset creation options are displayed. - Enter the following details for the cloud storage.
- Bucket Name
- Aws Access Key Id
- Aws Secret Access Key
File Directory URL (for the folder created by you on the S3 browser)
Filename or Wildcard
Notes:- By default, the number in the Skip Rows field is zero (0). You can enter an integer value in the field corresponding to the number of rows in the dataset you wish to delete.
- For example, if you enter 15 in the Skip Rows field, the first 15 rows will be skipped/deleted while creating the dataset.
- The administrator provides Aws Access Key Id and Aws Secret Access Key.
- If a file is already present in the root directory, you can access the file from the folder using a slash (/) symbol.
- If a folder is already present, you can give its path in the File Directory URL field.
- The File Directory URL is for the folder created by you on the S3 browser. This folder contains the dataset files whose Filename/Wildcard is mentioned in the next field.
- You can use special characters/symbols to search file names like an asterisk (*) and question mark (?).
- An asterisk (*) symbol searches file names with multiple (any number) characters in the specified place.
- For example, a filename with Data_*_* searches all file names containing multiple characters between the underscore marks and after the last underscore mark.
- A question mark (?) is used to search file names with a single character in the specified place.
- For example, a filename with Data_? _??? searches all file names containing one character between the underscore marks and three characters after the last underscore mark.
- Hence, a filename with Data_??_* searches all file names containing two characters between the underscore marks and multiple characters after the last underscore mark.
- You can search for the dataset files in all folders and sub-folders of the root directory by selecting the Traverse Subdirectory checkbox.
- To validate the connection parameters, click Verify.
If the parameters are valid, a Verification Success message is displayed. Also, the Show Filename(s) button gets activated. - To see the files detected, click Show Filename(s).
The list of detected files is displayed in a separate window.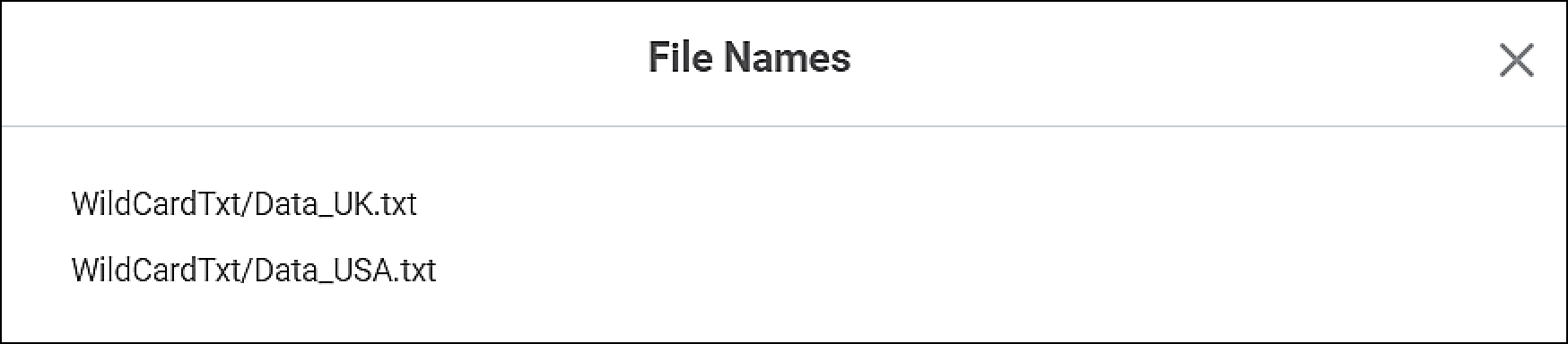
Also, the features (columns) in the Text worksheet are displayed in the Features box. To change the datatype of the features, refer to Configuring Feature Type.
If you wish to remove any of the features, hover over the feature name, and click the Close icon (
 ).
).
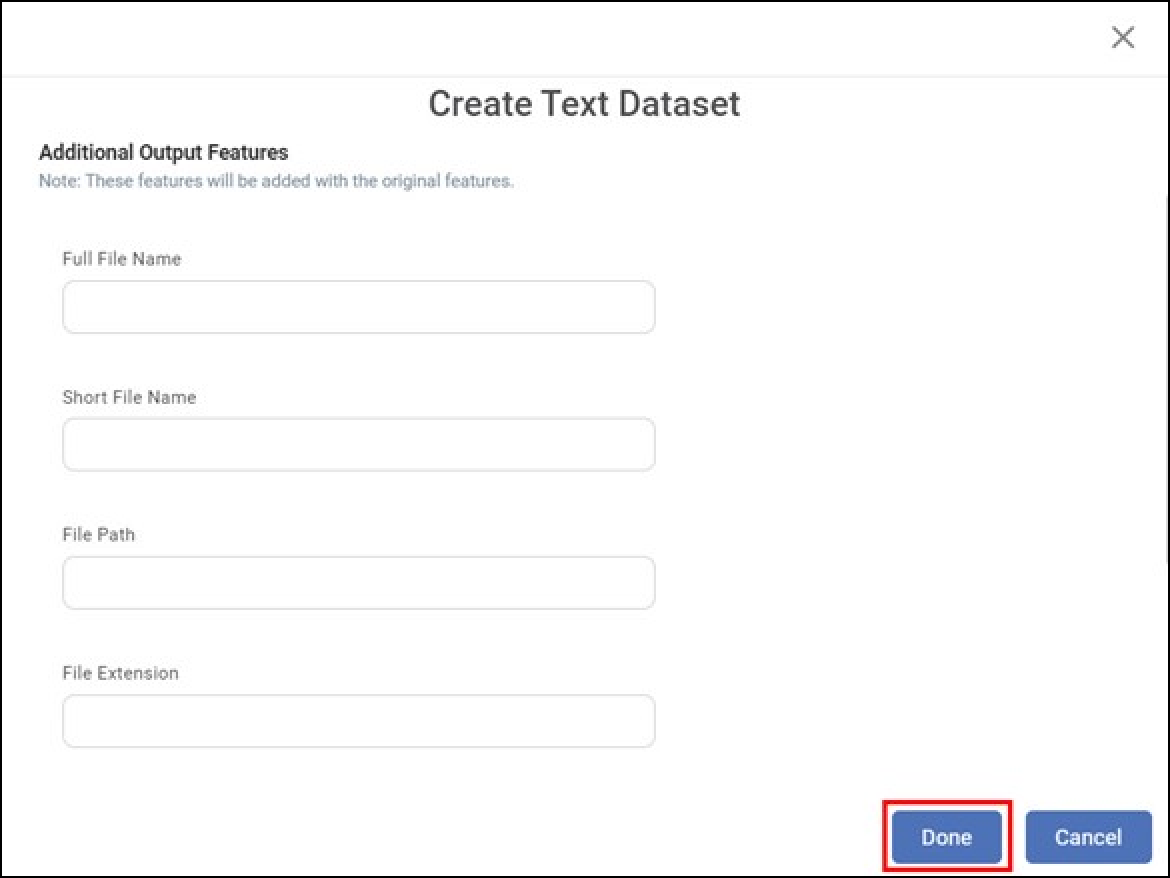
To insert additional features (along with the features already present in the dataset), click Additional Output Features.
Create Text Dataset window is displayed. It displays the following features, which can be inserted along with the existing ones.- Full File Name
- Shot File Name
- File Path
- File Extension
- File Size
- File Last Modified Date
Notes:
- The Additional Output Features are not selected by default.
- You can choose anyone, multiple, or all of them to be inserted into the dataset.
- Select the checkboxes corresponding to those features that you want to insert and click Done.
- Click Create.
Notes: |
|
The Text dataset is created in the current workspace and is available for use in workbooks, workflows, and dashboards.
Related Articles
Text
The Text formatting option is available in the Text widget. The table given below describes different fields present on Text widget formatting. Field Description Remark Text It allows you to edit the text shown in the Text Chart. — Text Font It ...Text Background
In RubiSight, three Background formatting options are available for Text Widget. Gradient Image Border The Gradient and Image formatting options can be applied independently. Border can be applied along with both, Gradient and Image. The Background ...Generate Smart Insights with Text/Image Processing
Smart Data Insights - Dashboard Data vs External Text/Image: RubiAI allows you to generate Smart Insights wrt dashboard data and the uploaded Text/Image file. You can attach any file in the text formats- word, , csv, excel, pdf, text and image ...Highlight- Option for Fetch Original Text Formatting
The Fetch Original Text Formatting option allows you to apply highlight settings using the text formatting already defined at the column level. When clicked, it retrieves formatting attributes such as font type, font size, bold, italic, and ...Formatting Custom Charts
RubiSight provides three charts which are different than the rest of the charts. They are - Text HTML Image