While
To use the While condition, follow the steps given below.
- Open the required workbook or create a new workbook. The selected workbook canvas is displayed.
- Add the reader/dataset if not already present in your workbook.
- Drag-and-drop or double-click the While node from Condition into the workbook canvas.
To create a workbook using the While loop, follow the steps given below.
- Connect the reader to the While node.
- Drag-and-drop or double-click the desired algorithm into the workbook canvas. Refer to Building Algorithm Flow in a Workbook Canvas.
- Connect the While node to the algorithm.
Connect the algorithm node to the End node.
Note:The algorithms should always be inserted between the Condition and the End node.
- Click the While node and select the Properties displayed on the right-hand side. Refer to While Condition Properties
- Click the algorithm node and select the Properties displayed on the right-hand side. Refer to Understanding the Algorithm Properties.
- Click the End node and select the Properties displayed on the right-hand side. Refer to End Properties.
- Click the Save icon () on the Function Pane of the workbook to save the workbook.
- Click the Run icon () on the Function Pane of the workbook To run the workbook. A sample workbook using the While loop is shown below.
The algorithm connected to While is executed until the While condition is true.
While Condition Properties
The While Condition Properties show Task Name fields and Clause fields associated with it.
The table given below describes the functions present on the While condition.
Field Name | Description | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
Task Name | It is the name of the condition selected (While). | — | |
While Tasks | It lets you select the successor algorithms which are executed while the condition evaluates to True. | — | |
Clause | It lets you create a complex condition. | You can add more than one clause. | |
Clause | Parameter | It lets you select the variable for the condition. |
|
Condition | It lets you select the mathematical operator for your variable. | — | |
Value | It lets you enter the required values to test or execute the successor algorithms connected to the While condition. | This value is compared with the Current Value of the added variable to evaluate the expression. | |
Notes: |
|
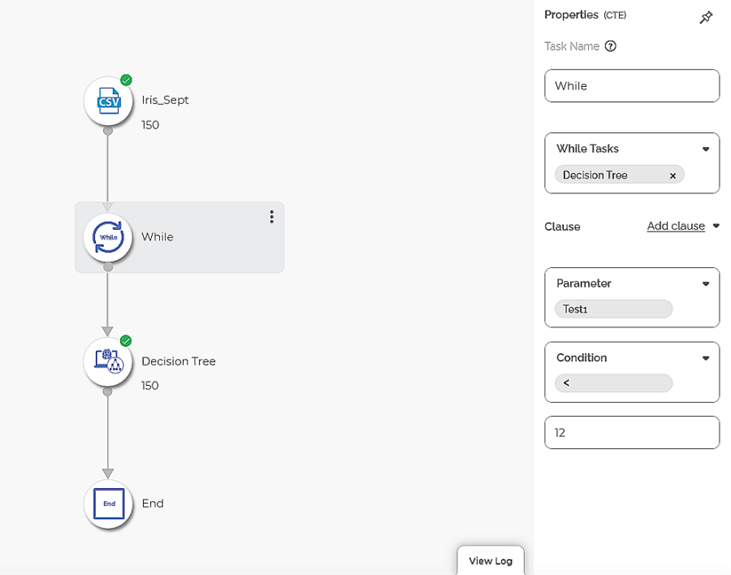
The figure given below is an example of While Properties. The selected condition is While, and the successor algorithm selected to execute the While condition is Decision Tree.
In the example above, the newly added variable is Test1 with the Current Value as 10. The While condition is Test1 <12. In this example, the Decision Tree algorithm is executed twice until the current value of Test1 is less than 12. In the third iteration, the current value becomes 12, the while condition fails at this point, and the execution stops.
Related Articles
Data Compare
Data Compare is located under Model Studio ( ) in Data Preparation, in the task pane on the left. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis. In the Data ...Discover
Discover is located under Rubi AI, in the task pane on the left. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis. In the Discover algorithm, you can only use ...Congifuring Feature Types
While creating a dataset of File type, you can change the variable type of the features displayed in the Features box. After selecting a file, the features in it are displayed in the Features box. To configure the variable type of a feature, follow ...Text
Creating Text Dataset To create a Text dataset, follow the steps given below. On the home page, click Create icon . The Product Selection page is displayed. Hover over the Data Connect tile and click Create Dataset. Dataset Selection page is ...Geographical Variables
In RubiSight, you can use Numerical, Textual, Interval, Categorical, and Geographical types of variables. Creating a Dataset with Geographical Variable Type To create a dataset containing a geographical variable type, follow the steps given below Add ...